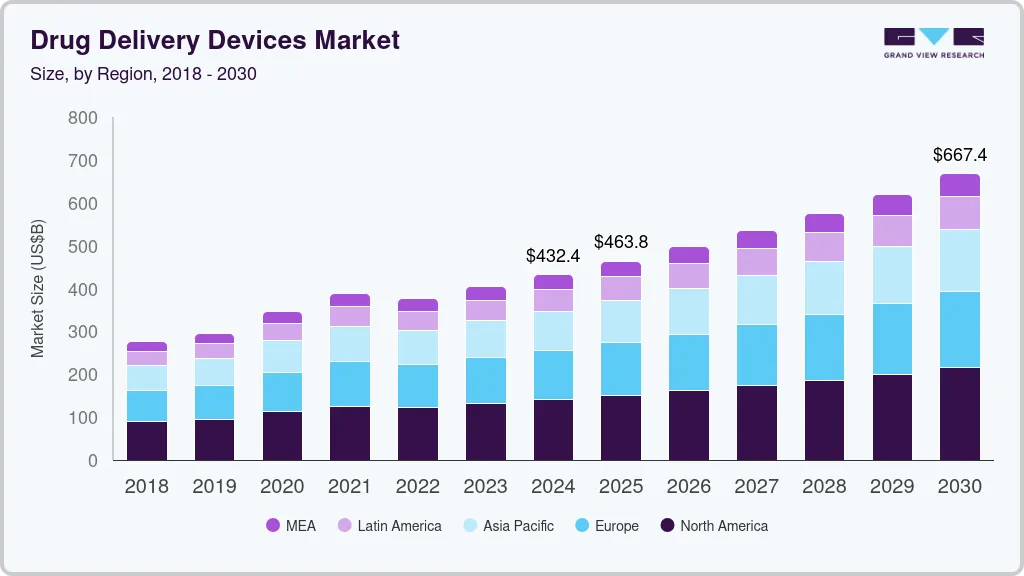
The global injectable drug delivery market is projected to surpass $1 trillion by 2030, rising from a valuation of approximately $690 billion in 2024. This growth is largely driven by the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, a surge in demand for biologics, and a growing preference for self-administration among patients. The transition from intravenous (IV) to subcutaneous (SC) delivery is being accelerated by the need for personalized medicine and the development of more sophisticated delivery systems that can handle complex drug regimens.
As chronic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer account for over 74% of annual deaths, the demand for advanced injectable drug delivery technologies is critical. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of integrating formulation science with device engineering to streamline development processes and enhance flexibility in therapy delivery. This shift not only aims to improve patient outcomes but also to reduce the burden on healthcare systems by facilitating at-home self-administration.
Use the database as your supply chain compass →