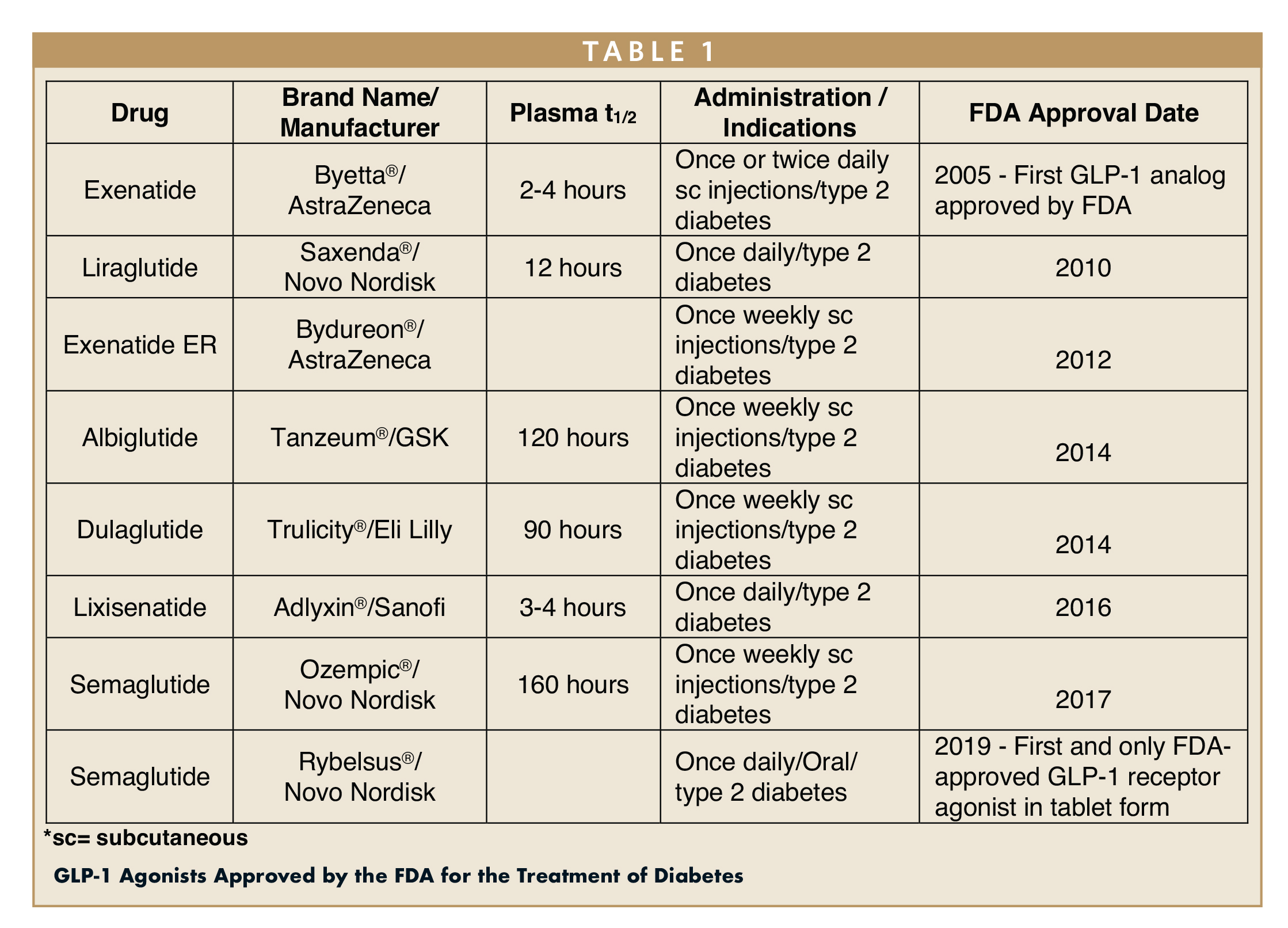
Recent advancements in drug delivery systems for Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are poised to significantly enhance medication adherence and treatment outcomes for obesity and type 2 diabetes. With over 890 million adults affected by obesity globally, the need for effective treatment options is critical. Traditional GLP-1 formulations face challenges such as frequent injections and gastrointestinal side effects, which can hinder patient compliance. Innovative delivery methods, including prolonged-release injectables, oral formulations, and transdermal systems, are being developed to address these issues.
These new approaches not only aim to improve the therapeutic efficacy of GLP-1 agonists but also strive to make treatment more accessible and patient-friendly. For instance, oral Semaglutide, the first oral GLP-1 receptor agonist, has demonstrated the potential for improved patient adherence despite lower bioavailability compared to its injectable counterparts. As pharmaceutical companies continue to explore advanced delivery mechanisms, the implications for patient care and treatment success in obesity management are substantial, potentially transforming the landscape of GLP-1 therapy.
Get started today with Solo access →