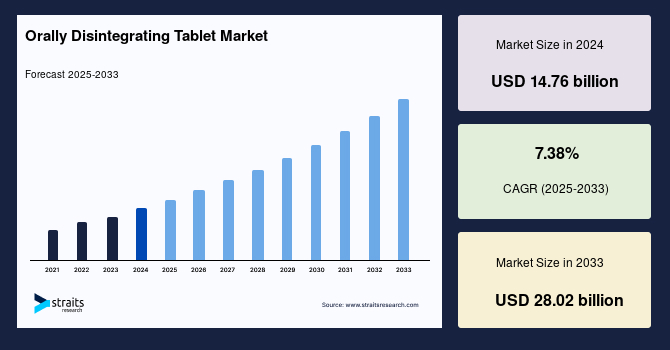
Orally disintegrating tablets (ODTs) are gaining traction in the pharmaceutical market, with projections indicating growth from $11 billion to over $27 billion by 2025. This surge is largely attributed to the needs of pediatric and geriatric populations, as well as patients with dysphagia, who require alternative dosage forms that facilitate easier administration. The United States Pharmacopoeia defines ODTs as tablets that disintegrate in less than 30 seconds, while the European Pharmacopoeia specifies a similar timeframe for orodispersible tablets. The rapid disintegration is achieved through excipients that exhibit high porosity and compressibility, which are critical for enhancing drug absorption.
However, the formulation of ODTs presents unique challenges, particularly in achieving effective taste-masking and maintaining stability under various storage conditions. The selection of excipients is crucial, as they must not only facilitate rapid disintegration but also ensure a pleasant mouthfeel and stability of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). As the demand for ODTs increases, pharmaceutical companies must navigate these complexities to optimize their formulations, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while meeting patient needs. The ongoing development of advanced excipients and manufacturing technologies will be pivotal in addressing these challenges, ultimately expanding the therapeutic applications of ODTs.
Open the full market picture for your next decision →